The story of DATEV and how it became an unshakable power in German accounting.
Dec 4, 2025
DATEV is more than software – it is the infrastructural foundation of German accounting. The text shows how a cooperative of tax advisors became the central backbone of accounting and payroll through regulatory entanglement, standardization, and decades of trust-building. At the same time, it explains why this very structure is hindering innovation today: closed data architectures, high switching costs, and a system built for stability rather than AI-based automation. A look at how the past and present shape digital progress.
Ready for payroll that finally takes the pressure off?
Leave your contact details - we will get back to you shortly.
The Story of DATEV and How It Became an Unshakeable Power in German Accounting
Introduction
Anyone who starts or runs a business in Germany eventually experiences the moment when a tax advisor, a payroll service provider, an auditor, or a bank requests a specific format. The conversation often begins with a shrug and ends with five words that mark entry into a typically German universe. They say: "We need the DATEV export." It doesn’t matter which software the founder has chosen or which cloud tools the company prefers. Everything ultimately runs back to the cooperative founded decades ago in Nuremberg. This moment is the first indication that DATEV is not just software. It is infrastructure.
Understanding how DATEV reached this position requires a look at German administrative culture. The country has built a regulatory machine that prioritizes precision over experimentation, standardization over diversity, and proven reliability over quick iteration. In this environment, DATEV evolved from a simple batch processing system of the 1960s to the digital backbone of tax, accounting, and payroll processes. DATEV did not grow because it outperformed others through classic market mechanisms. It grew because it internalized the regulatory DNA of the German system.
This article highlights this story and connects it to present realities. As Germany faces AI-driven payroll systems, real-time compliance, and new digital expectations from younger companies, DATEV's legacy is both an advantage and a limitation. The cooperative has established a foundation of trust, but at the same time limits the country’s ability to implement modern, AI-based payroll automation. In the end, it becomes clear how a single institution can stabilize and also hinder an economy.
Definitions and Legal Background
DATEV eG was founded in 1966 by 65 tax advisors who wanted to create a joint electronic data processing center at a time when computing power was extremely expensive. They established a cooperative, not a commercial company. This structure ensured that control remained entirely in the hands of the licensed tax advisors. From the very beginning, DATEV was closely intertwined with German law, particularly the Tax Advisory Act, which grants tax advisors exclusive rights for certain declarations and representations. This legal barrier fortified DATEV because only tax advisors were allowed to produce state-accepted submissions, and they almost exclusively chose DATEV.
The cooperative grew steadily. By 1970, it was already serving several hundred firms. In the 1990s, it was tens of thousands. Today, DATEV has over 40,000 cooperative members, covering a large part of the approximately 60,000 tax advisors in Germany. Through these members, DATEV indirectly serves more than 2.5 million businesses. The revenue also reflects this scale. In 2023, DATEV generated around 1.3 billion euros, more than many publicly traded software companies in Europe. DATEV never needed venture capital, aggressive sales teams, or marketing battles. Growth directly followed from its structural integration with the regulatory framework.
The cooperative model provides tax advisors with both influence over governance and financial incentives. Members vote on leadership and receive dividends. This creates loyalty that is stronger than any B2B software contract. Legally, DATEV's central role is reinforced by the state. German tax and payroll accounting requires precise, validated data structures. DATEV's software reflects these structures. Changes in the law are directly incorporated into the systems. Tax advisors rely on DATEV not only for convenience but also for legal certainty and risk minimization.
This legal-regulatory environment explains why DATEV's dominance is not merely a market outcome. It is a structural component of German economic administration.
Who Is Affected
Tax advisors are DATEV’s most important stakeholders. Their firms rely on DATEV modules for accounting, VAT returns, annual financial statements, payroll processing, document archiving, and regulatory communication. A typical tax advisor uses ten to twenty DATEV modules that interlink. Switching to another system would disrupt decades-old processes. Moreover, cooperative members would lose dividends from DATEV's success. This combination of operational dependency and economic participation creates a particularly strong form of lock-in.
Businesses are indirectly but massively affected. A founder can choose a modern cloud accounting platform. They can track expenses, automate payments, integrate bank feeds, and create dashboards. But at the end of the year, the tax advisor requests the DATEV export. If the company's tool cannot provide this, the advisor either demands additional effort or forces the company into DATEV-compatible processes. The founder's software flexibility shrinks.
Especially foreign founders are surprised. They expect that software choices are made internally. In Germany, the choice is made by the tax advisor, and their system is almost always DATEV. International companies must adapt to a tool their teams have never heard of before, with structures that differ significantly from software in the US, UK, or Nordic markets.
Payroll professionals also experience this dependency. DATEV LODAS and DATEV Payroll are central payroll systems in Germany. Even if teams use alternative payroll tools, final submissions require DATEV-compatible outputs. This often necessitates parallel processes.
Startups in the accounting or payroll market face the toughest barriers. DATEV's interfaces, certifications, and data formats reflect decades of cooperative logic. They are not designed for rapid integration or open automation. Building modern payroll engines requires navigating this complexity, slowing innovation and increasing costs.
What’s Changing: Then vs. Now
DATEV's evolution mirrors the development of German administrative technology. In its early years, DATEV processed punch cards sent by mail. Results came back days later. The value lay not in speed but in standardization. In the 1980s, DATEV expanded its offerings to software packages. By the 1990s, extensive module libraries were already available. The reunification further increased the demand for unified systems.
Today, DATEV looks completely different. With Companies Online, over 800,000 businesses use the DATEV cloud. Additionally, there are tools for document management, audit preparation, payroll, digital signatures, and more. The entire ecosystem creates a structure that deeply connects advisors and businesses with DATEV.
New providers present a different picture. Pennylane, Integral, Candis, and numerous AI platforms offer real-time collaboration, API-based automation, and modern user interfaces. They provide features like transaction audit trails, automatic SEPA files, and live financial analyses. They meet global expectations for controlling and accounting software.
But they operate within DATEV's gravitational field. No matter how advanced they are, they must deliver DATEV exports, transfer data into DATEV structures, or align processes with DATEV definitions. Even AI tools must accept DATEV's logic. This reveals a deeper truth. DATEV does not compete with new tools. DATEV defines the rules of the game.
Practical Implications for the Target Group
Businesses particularly feel DATEV's influence during system changes. Implementing new accounting software is straightforward until the tax advisor requests DATEV formats. Payroll teams use modern cloud engines until audits begin, and auditors demand DATEV data. Finance departments test AI-based reconciliation tools, but DATEV's closed architecture hinders the data access needed for AI.
G2 reviews illustrate this tension. Users praise DATEV’s reliability and regulatory accuracy. They emphasize that the system remains stable during legislative changes and provides strong audit trails. Yet, just as frequently, they criticize outdated interfaces, poor performance, limited integrations, and illogical workflows. A recurring statement is: "We are dependent, not convinced."
§108 GewO explains this behavior. Employers must provide correct payroll statements promptly. The complexity of German payroll regulations makes this challenging. DATEV has embedded these rules deeply in its system. Using alternative tools increases the risk of errors. This legal pressure reinforces DATEV's position.
Audits also strengthen the dependency. Auditors prefer standardized structures. They know DATEV reports. When companies use different systems, auditors often request additional verification. This increases effort and risk. Tax advisors therefore systematically recommend using DATEV.
AI-driven payroll automation encounters DATEV's limitations. The systems do not provide event-level data access that modern AI requires. The architecture is based on batch-oriented processes. This slows innovation and makes Germany structurally less competitive than more open systems.
Case Studies
DATEV's growth can be illustrated with numbers. Starting with 65 founding members, the cooperative grew to around 10,000 members by 1980. By 1995, there were over 30,000, today more than 40,000. Germany has about 3.5 to 3.7 million active SMEs. If DATEV indirectly serves 2.5 million companies through its members, that represents a market share that few other software worldwide achieve.
Companies Online has over 800,000 users. DATEV's payroll engines process millions of paychecks monthly. With 1.3 billion euros in annual revenue, DATEV is one of the largest software organizations in Europe without external financing.
The switching costs explain the stability. A tax advisor with fifteen DATEV modules would require seven months to fully switch, assuming two weeks of transition effort per module. Employee training, workflow reconstruction, revalidating reports, and integrations would consume enormous resources. G2 ratings reflect this. Many would switch but not under bearable conditions.
Payroll processing is even more complex. Companies lose historical logic, SEPA files must be re-modeled, and payroll tax and social security calculations must be re-validated. Without open data structures, AI remains ineffective. Companies remain trapped in the old system.
Special Cases or Exceptions
Foreign founders often underestimate the peculiarities of the German software landscape. They expect compatibility with common formats. Instead, they encounter a monopolistic basic infrastructure. DATEV is not just an option. It is the standard.
Startups in the AI and fintech sector face the same challenges. Without access to deeper DATEV structures, they can only deliver partial values. They lack the foundation for holistic automation.
In insolvency cases, courts and experts insist on DATEV. Stability counts more than innovation. New tools could create confusion, hence DATEV remains unchanged.
Even tax advisors wishing to modernize face barriers. Teams know DATEV. Clients expect DATEV evaluations. Cooperative incentives hinder breakthroughs. Innovation remains limited to pilot projects.
Payroll teams in hybrid systems work efficiently internally, but the year-end compels them back into DATEV formats. This dual burden illustrates the structural dependency.
How This Story is Interpreted Today
DATEV's story reflects German values. Stability, compliance, professionalized responsibility. DATEV became strong because it clung to the state. It provided reliability during times of regulatory change. It offered continuity. It codified legal certainty in software.
Yet this strength creates limits today. AI requires clean, structured, event-based data. Modern payroll demands real-time processing. Compliance calls for integrations with banks, HR systems, and tax channels. DATEV’s architecture does not meet these requirements. Its structure has historically evolved, not been rethought. Cooperative governance amplifies inertia. Security replaces innovation pressure.
§108 GewO further strengthens the dependency. Companies use tools that minimize risk. Auditors trust DATEV. Everything outside the ecosystem feels risky.
The AI revolution reveals the fundamental problem. Germany’s ability to build modern payroll systems depends on systems designed for a different era. Startups deliver impressive models but fail due to the closed data architectures. DATEV is both the guardian and bottleneck of financial digitalization.
The interpretation is systemic, not emotional. The story explains why Germany trusts DATEV. It also explains why Germany struggles to break free from it.
Conclusion
The story of DATEV is the story of German administration. A cooperative founded in 1966 evolved into a billion-euro organization because it intertwined with the regulatory structures and cultural preferences of the country. It brought order and trust to a complex world.
Yet this very story shapes Germany's future. DATEV stabilizes but also slows down. AI-based payroll, cloud accounting, and integrated financial systems must adhere to structures created for an earlier time. For genuine digitalization, Germany needs both new software and new expectations around data openness.
DATEV is neither a hero nor a hindrance. It is a historical product, a mirror of German bureaucracy, and a central element of the economic infrastructure. Understanding how it arose helps to recognize why change is difficult and how future innovation can only occur through a respectful yet bold engagement with this past.
Sources
Why is DATEV still so dominant in German accounting today?
DATEV's dominance is not a classic market result, but rather the outcome of strong regulatory intertwining. Since its founding in 1966, DATEV has been directly linked to German tax and professional law – particularly to the Tax Consultancy Act, which assigns exclusive tasks to tax consultants. As nearly all tax consultants are members of the cooperative and use its software, a network and trust effect is created that structurally excludes new providers. Auditors, banks, and authorities have adapted their processes to DATEV formats over decades – which has made DATEV de facto the nationwide standard. Even modern cloud tools must align with this.
What does the DATEV dependency specifically mean for companies?
While companies can use modern accounting or payroll tools, there is hardly a way around DATEV in central processes. Tax advisors almost always require a DATEV export at the end of the year, auditors demand DATEV evaluations, and payroll reports must be provided in DATEV-compatible structures. If the software used does not support this, it leads to additional effort, often even a technical or organizational setback. Particularly, international companies underestimate this effect – they must translate into the German DATEV logic regardless of their global tools.
Why does DATEV complicate modern AI innovations in the area of payroll?
DATEV was historically designed as a batch-oriented, closed system and not as an API or event-driven real-time ecosystem, as would be necessary for modern AI applications. The lack of data openness, proprietary structures, and complex integration requirements make it difficult for startups to build automated payroll engines or AI-supported accounting processes. At the same time, auditors and tax advisors still prefer DATEV due to its high regulatory compliance. The result: Germany has extreme stability but lower innovation speed. While AI can build on DATEV, it cannot operate at full potential.
Aaron H.
Further articles
Feb 9, 2026
·
Payment
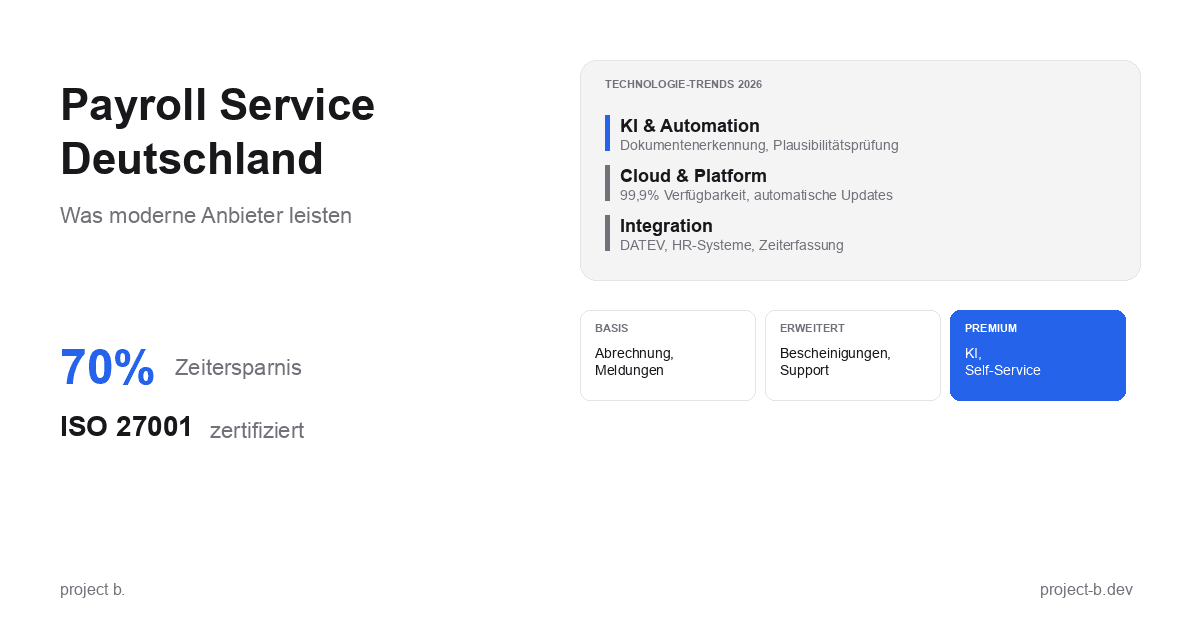
Payroll Service Deutschland: Was moderne Anbieter leisten
Payroll Service in Deutschland gesucht? Erfahren Sie, was moderne Anbieter leisten, welche Technologien sie nutzen und worauf Sie bei der Auswahl achten sollten.
Feb 11, 2026
·
Outsourcing
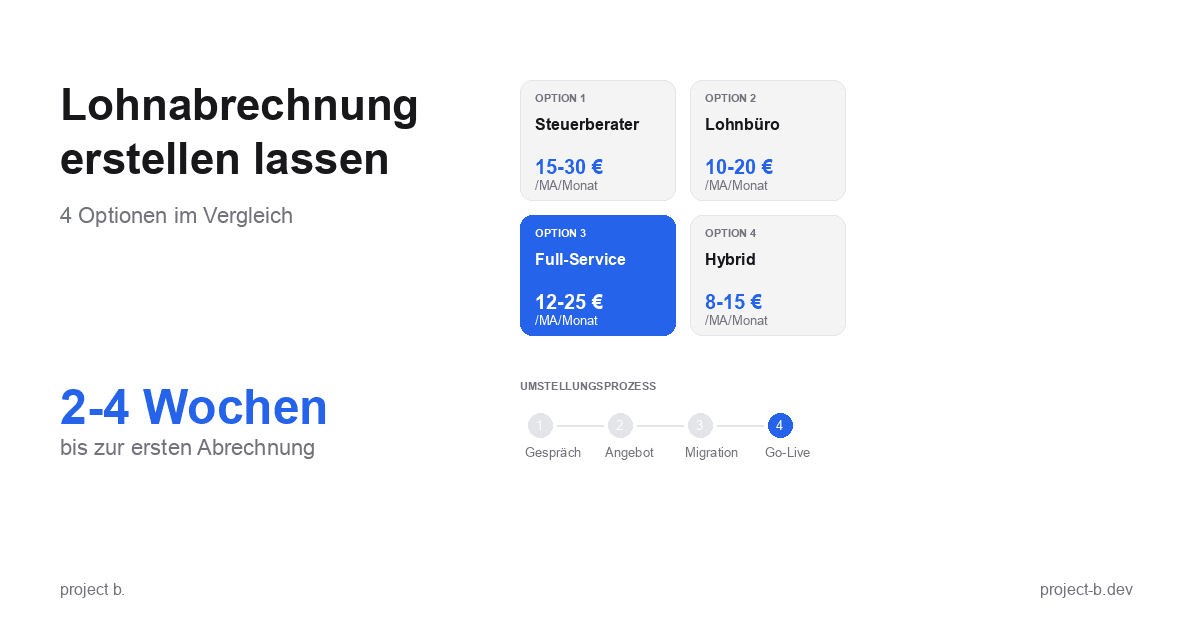
Lohnabrechnung erstellen lassen: Ihre Optionen im Vergleich
Lohnabrechnung erstellen lassen statt selbst kämpfen? Erfahren Sie, welche Optionen Sie haben, was es kostet und wie schnell Sie starten können.

Feb 9, 2026
·
Outsourcing
Lohnabrechnung Dienstleister: So finden Sie den richtigen Partner
Lohnabrechnung Dienstleister gesucht? 7 Kriterien für die Auswahl, Preisvergleich und Checkliste fürs Erstgespräch. Finden Sie den Partner, der zu Ihnen passt.
Feb 6, 2026
·
Outsourcing
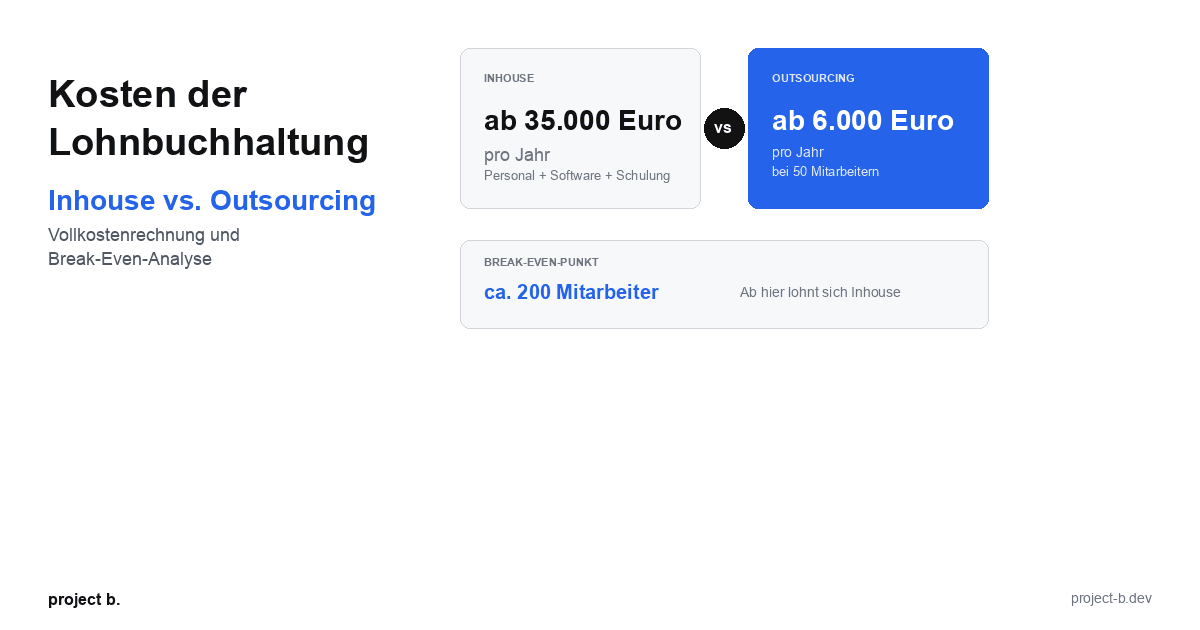
Kosten der Lohnbuchhaltung: Inhouse vs. Outsourcing im Vergleich
Lohnbuchhaltung Kosten: Inhouse ab 35.000 Euro/Jahr vs. Outsourcing ab 6.000 Euro/Jahr. Break-Even-Analyse, ROI-Rechnung und Entscheidungshilfe.
Feb 4, 2026
·
Outsourcing
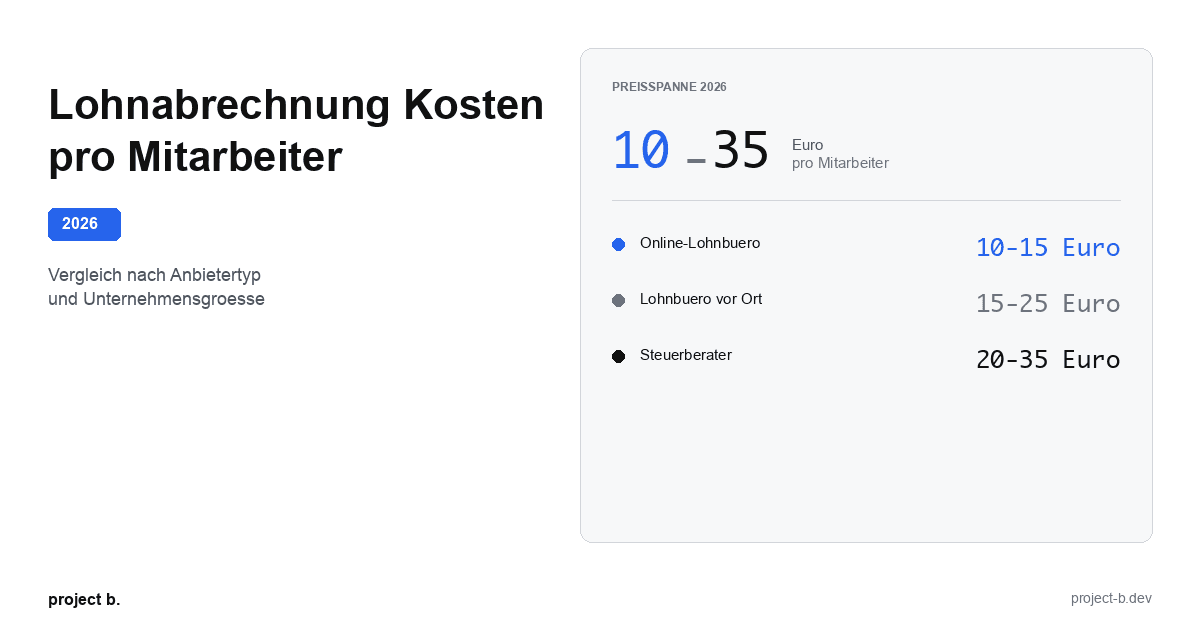
Lohnabrechnung Kosten pro Mitarbeiter: Was Sie 2026 zahlen
Lohnabrechnung Kosten 2026: 10-35 Euro pro Mitarbeiter je nach Anbieter. Vergleich nach Unternehmensgroesse, Branche und versteckte Kosten aufgedeckt.
Feb 2, 2026
·
Outsourcing
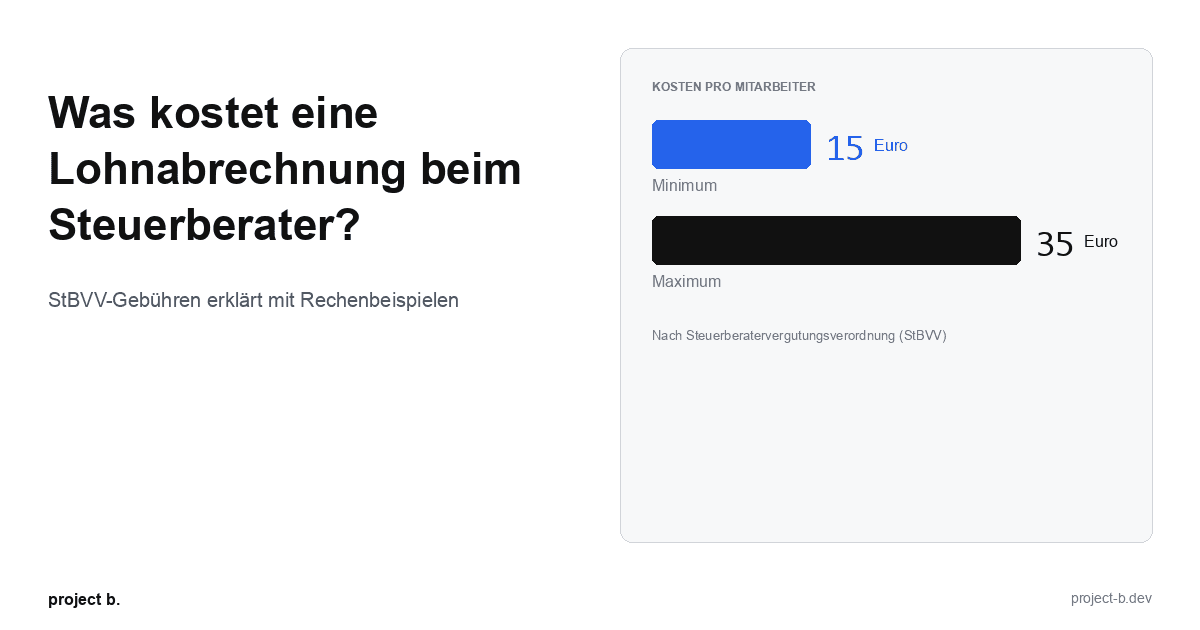
Was kostet eine Lohnabrechnung beim Steuerberater?
Lohnabrechnung beim Steuerberater: Kosten von 15-35 € pro Mitarbeiter. StBVV-Gebühren erklärt, Preisvergleich und Rechenbeispiele für 10, 50, 100 Mitarbeiter.
Jan 30, 2026
·
Outsourcing
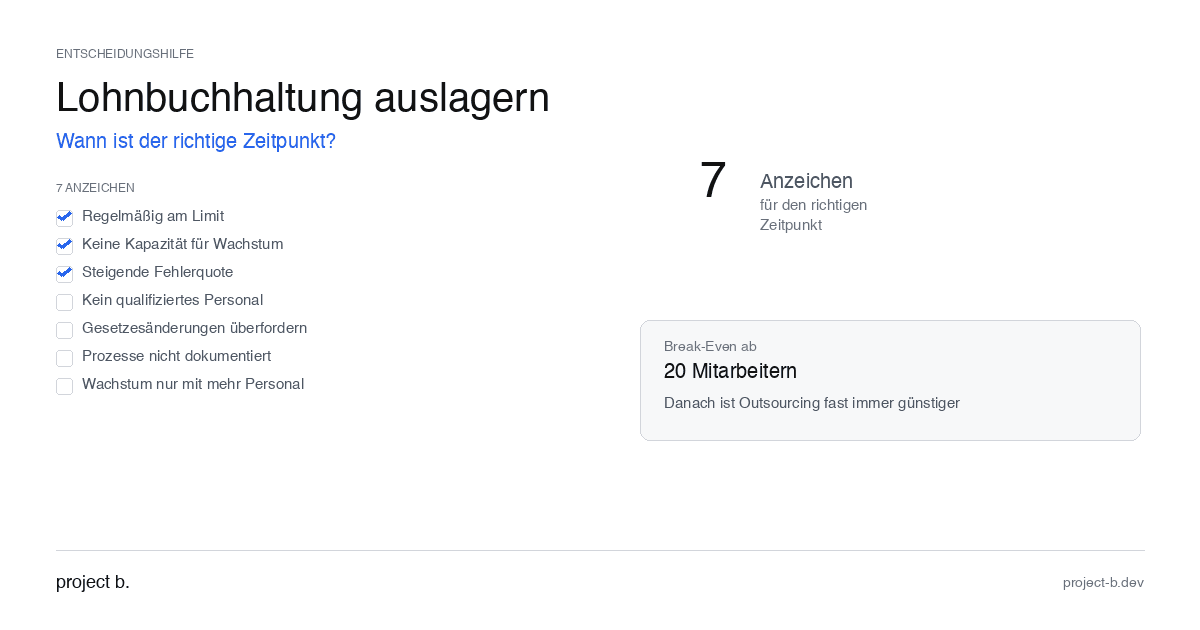
Outsource payroll accounting: When is the right time?
Outsourcing payroll: 7 clear signs that now is the right time. Including break-even analysis and DATEV integration check.
Jan 28, 2026
·
Outsourcing
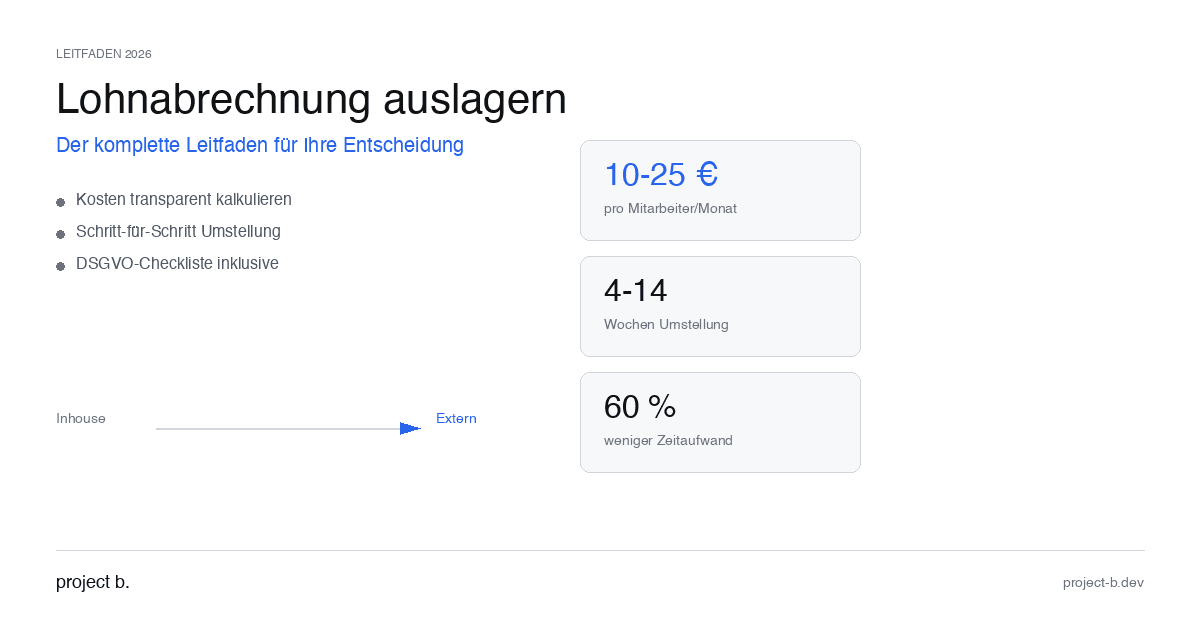
Outsourcing payroll accounting: The complete guide for 2026
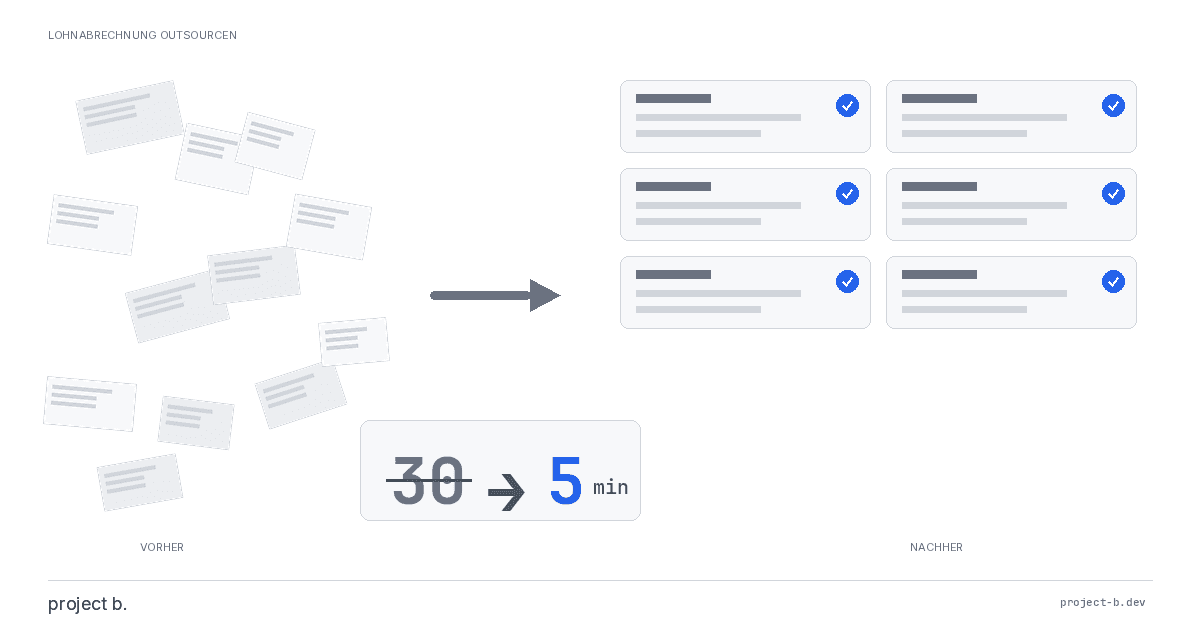
Outsource payroll processing 2026: Costs from €10 per employee, step-by-step guide and GDPR checklist. This is how to make the transition without risk.
Jan 26, 2026
·
Outsourcing
Outsourcing payroll: Costs, benefits, and providers at a glance
Outsource payroll accounting from €10 per employee. Learn about the benefits of outsourcing, its costs, and how to find the right provider.
Jan 22, 2026
·
AI
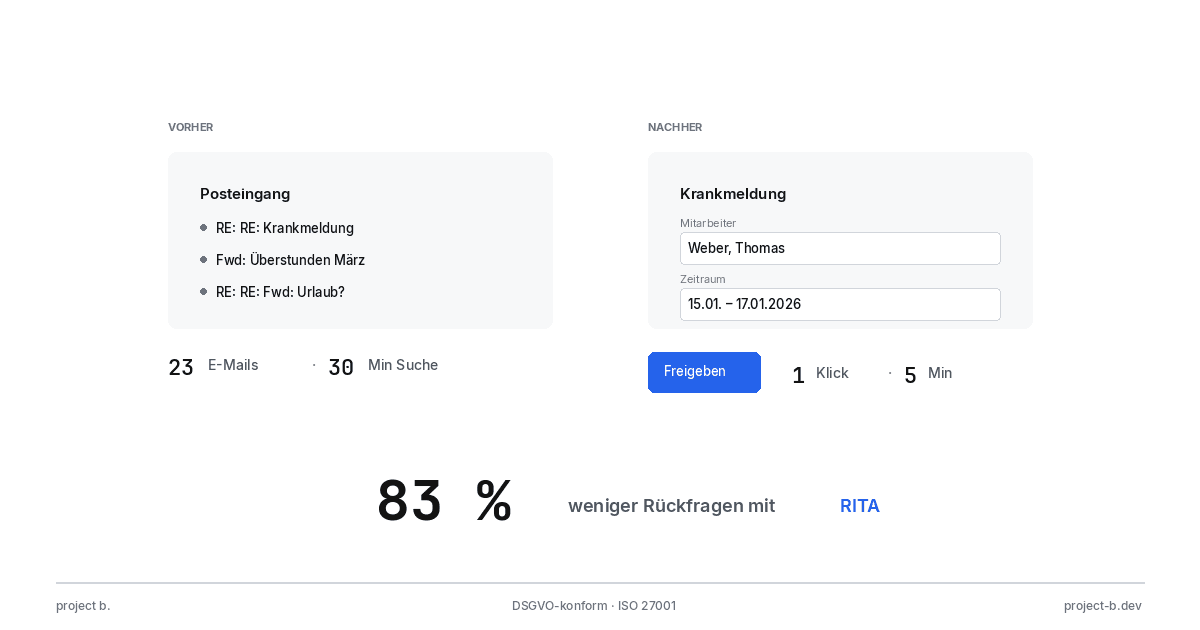
Client portal vs. Email chaos: What modern payroll processing is all about
Payroll statements by email pose a GDPR risk. With the project b. Portal and RITA, you save 1,400 hours/year. This is how secure data exchange works.

Jan 20, 2026
·
AI
From Excel to the Cockpit: How Payroll Offices Will Make the Leap into Digitalization in 2026
Digital payroll instead of Excel: With RITA and the project b. cockpit, payroll offices save 40% time without switching to DATEV. Practical guide with checklist.

Jan 15, 2026
·
Personal
ELStAM Procedure 2026: This is how the new private health insurance notification for employers works
From 2026, employers will report private health insurance contributions digitally via the ELStAM procedure. Find out which systems are affected and how you can prepare now.

Jan 14, 2026
·
AI
Active pension 2026: What payroll offices and HR departments need to prepare now
Pension from January 2026: Up to €2,000 tax allowance for retirees. Learn about the changes in payroll processes and how AI facilitates implementation.

Jan 13, 2026
·
AI
AI-Powered Payroll Software: How Tax Advisors Will Save Time in 2026
AI payroll accounting for tax consultants: Learn how project b. reduces manual work by 80% with RITA and helps combat the skilled labor shortage.

Jan 8, 2026
·
Payment
Personio vs. project b.: Which tool really fits your payroll?
Personio or project b.? Comparison for StartUps & Scaleups: DATEV integration, AI automation, costs. Why specialized payroll tools are gaining traction.

Jan 4, 2026
·
Payment
Power outage in Berlin: Why employers still have to pay wages
Power outage Berlin 2026: 2,200 businesses affected. Find out why employers must still pay wages according to § 615 BGB - and what applies to payroll.

Jan 5, 2026
·
AI
Payroll 2026: All Changes at a Glance (with AI Automation)
Minimum wage €13.90, mini-job limit €603, new contribution assessment ceilings: An overview of all changes for payroll in 2026. Learn how AI automatically implements these updates.

Dec 31, 2025
·
AI
AI in Payroll: Hype or Help?
AI in payroll processing: What is behind it? A guide for anyone who wants to understand the topic before making a decision.

Dec 29, 2025
·
AI
Payroll without professionals? This is how AI will help in 2026
AI in payroll: 70% less routine work, 0.1% error rate. This is how companies are solving the skilled labor shortage in payroll accounting in 2026.

Dec 26, 2025
·
AI
This is how you use AI in payroll.
Enough with manual data collection: This is how AI supports payroll accounting in case of sickness notifications, master data, and billing - without loss of control.
Dec 22, 2025
·
AI
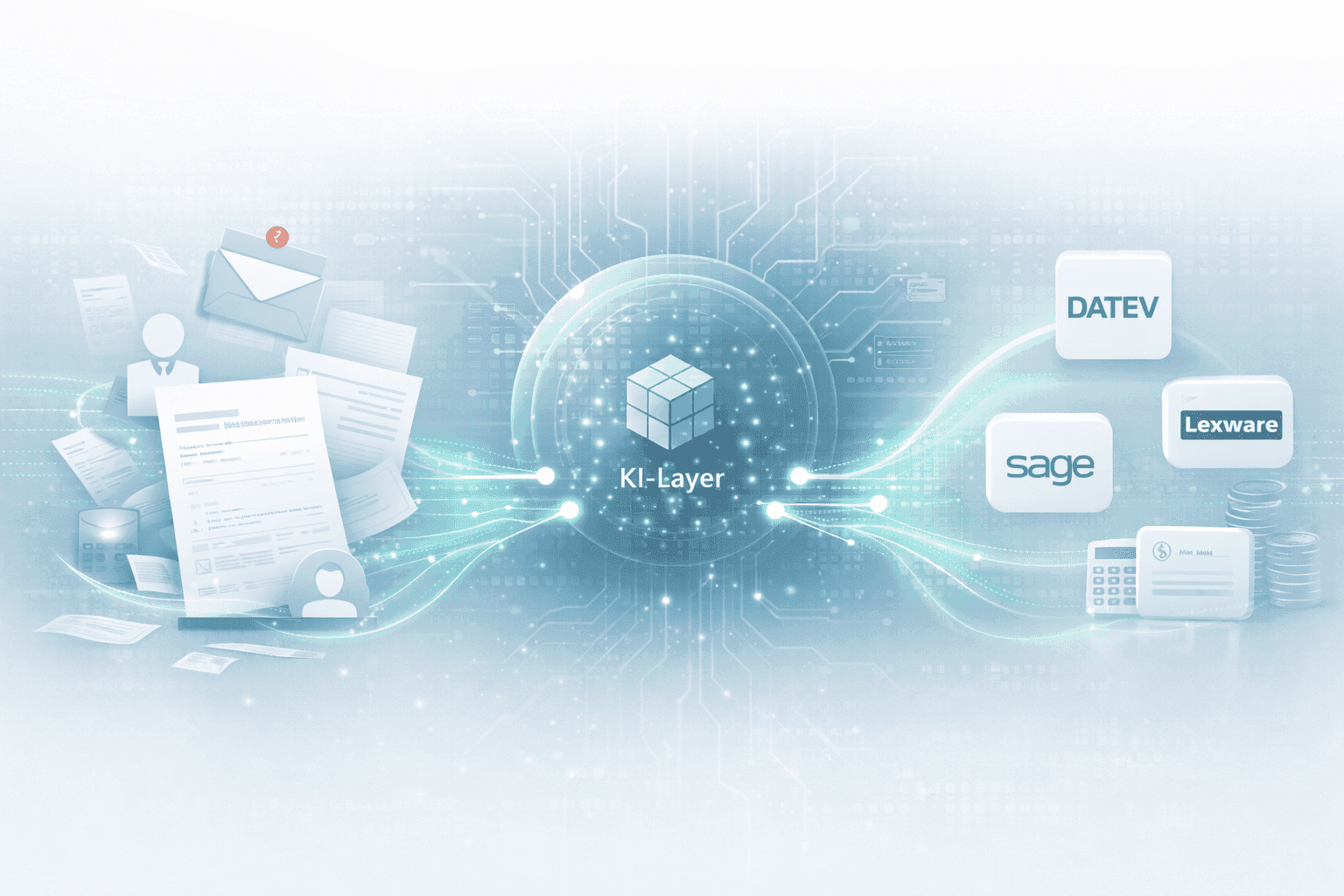
How an AI layer works in payroll.
Digital payroll, but manual data entry? An AI layer closes the gap between employees, HR, and DATEV & Co.

Dec 17, 2025
·
AI
Payroll accounting with AI: 5 terms that every payroll clerk should know
Payroll processing explained clearly with AI: These 5 key AI terms payroll accountants should know to automate processes, reduce errors, and work more efficiently.

Dec 10, 2025
·
AI
How companies automate payroll accounting with Rita
Learn how Rita from project b. has automated the preliminary payroll accounting. From data collection to DATEV integration: This is how payroll agencies and tax consultants save up to 70% time.

Dec 8, 2025
·
AI
AI Software for Payroll Accounting: The Ultimate Selection Guide
Discover the ultimate selection guide for AI software in payroll. Compare AI tools and find the best payroll software for your business.
Dec 2, 2025
·
AI
5 Reasons for Payroll Processing with project b.
Discover 5 reasons why tax consultants and payroll offices digitize their preparatory payroll accounting with project b. AI-assisted data collection, fewer queries, full DATEV integration.
Dec 5, 2025
·
AI
10 processes in payroll that AI is already handling today
Discover 10 payroll processes that AI has already automated: from master data validation to compliance monitoring. Save up to 94% time on digital payroll.
Dec 3, 2025
·
Payment
EU Salary Transparency Directive: How to Prepare Your Payroll for June 2026
Discover the best tools for implementing the EU Pay Transparency Directive – including AI solutions like project b. for fair and data-driven salary analyses.

Nov 25, 2025
·
AI
5 Easy Ways to Automate Payroll in 2026
5 practical ways to automate payroll: from digital time tracking to AI-driven software. With cost-saving examples for medium-sized businesses, tax consultants, and payroll offices.
Nov 26, 2025
·
AI
AI in payroll processing: What will be possible in 2026 and what will not?
AI in Payroll 2026: What can artificial intelligence really achieve in payroll? Reality check with maturity assessment, practical examples, and an honest analysis of the limits. For payroll offices, tax advisors, and SMEs.
Nov 27, 2025
·
AI
RPA vs. AI in Payroll: The Ultimate Technology Comparison 2026
RPA or AI in payroll accounting? The major comparison for 2026 shows advantages, costs, areas of application, and practical examples for the right automation strategy.
Nov 24, 2025
·
Payment
Pension flat-rate reform 2026: What employers need to adjust in their payroll software now
Major income tax reform from 2026: The retirement allowance will be recalculated. Learn how this affects net wages, payroll software, and employers.

Nov 18, 2025
·
Payment
Continuous Payroll 2026: How Real-Time Payroll Processing is Replacing Monthly Payroll Statements
Continuous Payroll revolutionizes payroll processing: real-time salary data, on-demand pay, and fewer errors. This is how SMEs and HR teams benefit in 2026.
Nov 20, 2025
·
Payment
Predictive Analytics in Payroll: How Tax Advisors Avoid Costly Mistakes
Discover how predictive analytics reduces error rates in payroll, saves costs, and transforms your payroll from reactive to proactive.

Nov 13, 2025
·
Personal
AI in Payroll Accounting: Practical Guide for Payroll Offices and Tax Advisors 2026
AI in Payroll Accounting 2026: Practical Guide for Payroll Offices with Software Comparison (project b., DATEV, Lexware), ROI Calculation and Step-by-Step Instructions.